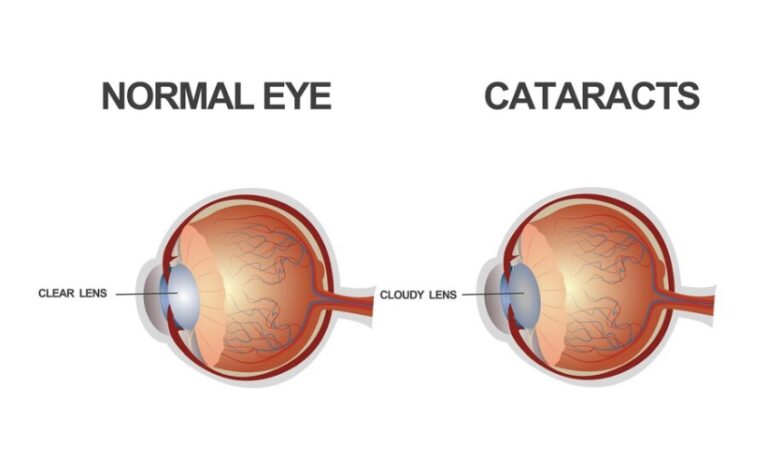
Cataracts occur when the natural lens of the eye becomes cloudy or opaque. This cloudiness prevents light from passing through clearly to the retina, leading to blurred or dimmed vision. Cataracts develop gradually, and the symptoms may worsen over time, making it difficult to perform daily activities and affecting overall vision quality.
Common symptoms of cataracts include:
Cataracts can develop due to various factors, including:
A comprehensive eye examination is necessary to diagnose cataracts. During the exam, our eye care professionals will:
Eyeglasses and Contact Lenses:
Surgical Intervention:
Preoperative and Postoperative Care: