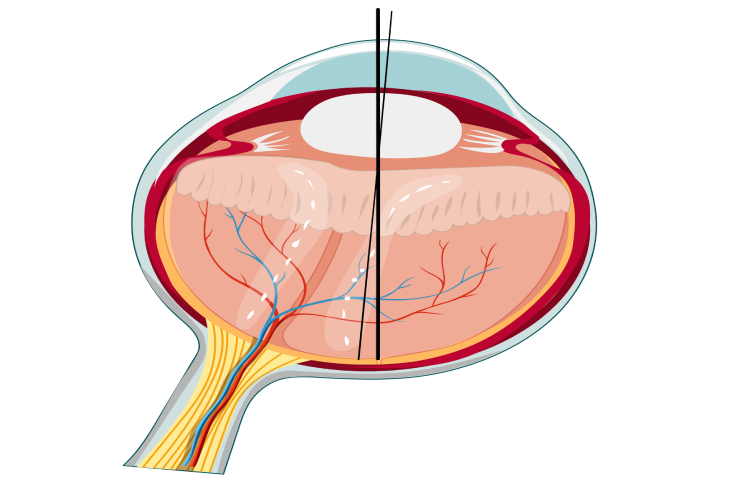
Retinal detachment occurs when the retina, the light-sensitive layer of tissue at the back of the eye, separates from the underlying supportive tissue. The retina is essential for converting light into neural signals that the brain interprets as vision. When it detaches, the retina can no longer function properly, leading to potential vision loss or blindness if not addressed quickly.
Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment:
Tractional Retinal Detachment:
Exudative Retinal Detachment:
Retinal detachment is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention. Symptoms may include:
Several factors can increase the risk of retinal detachment, including: